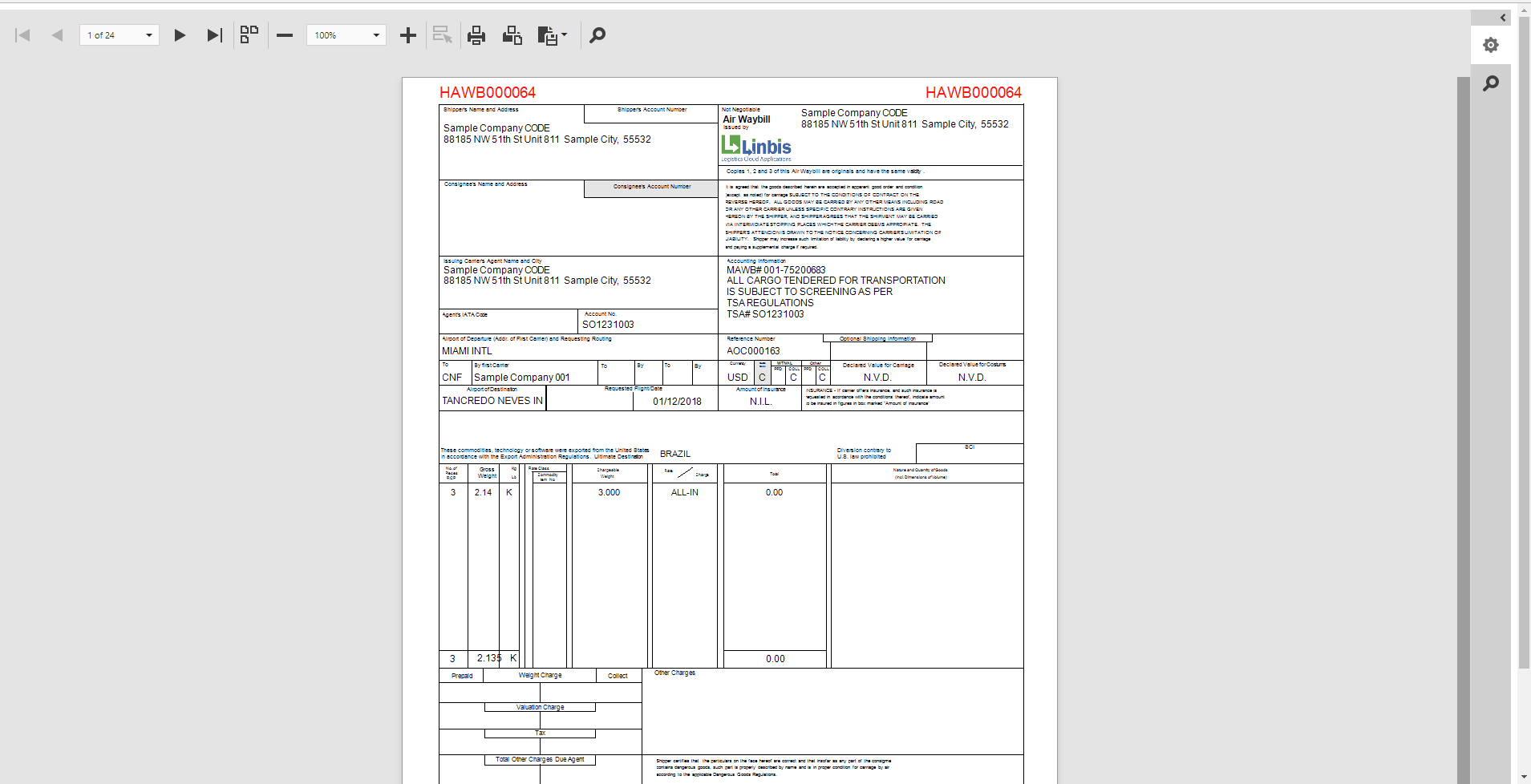
Master Airway Bill (MAWB)
In laymen terms an Airway Bill is a document, which is the proof of receipt of goods from the shipper and issued by the air carrier. An Airway Bill is the most important document issued by a carrier, directly or via any of its agents. It is a non-negotiable transport document that covers the transport of cargo from airport to airport.
Why Choose Us
Streamline Your Air Freight Management with Advanced HAWB/MAWB Software
In the fast-paced world of air freight logistics, accuracy and efficiency are not just goals—they’re necessities. Linbis HAWB/MAWB software is engineered to meet the demands of modern air freight forwarders, offering a suite of powerful tools designed to streamline operations, reduce manual errors, and elevate your service delivery.
Understanding HAWB and MAWB in Air Freight
- Generate HAWB and MAWB documents in a few clicks.
- Automate data entry with smart fields that reduce time and errors.
- Easily track shipments with real-time updates.
HAWB/MAWB Software
- Managing these critical documents can be a daunting task, which is where our software comes in.
- We provide a robust solution for generating, tracking, and managing HAWB and MAWB efficiently and accurately.
It's all about making your business goals a reality.
The world of air freight is complex, with various documentation and procedures that must be followed to ensure the smooth transit of goods across international borders. Two key documents in this process are the House Air Waybill (HAWB) and the Master Air Waybill (MAWB). Understanding these documents is crucial for shippers, freight forwarders, and students of logistics.
The MAWB is a legal contract between the shipper and the carrier. It's issued by the main carrier of goods on international flights and often goes from the airport of departure to the airport of arrival.
It serves as a receipt of goods by an airline, confirming the carrier has received the cargo as described and is obligated to deliver it. The MAWB is non-negotiable and typically consigned to a corresponding agent at the destination.

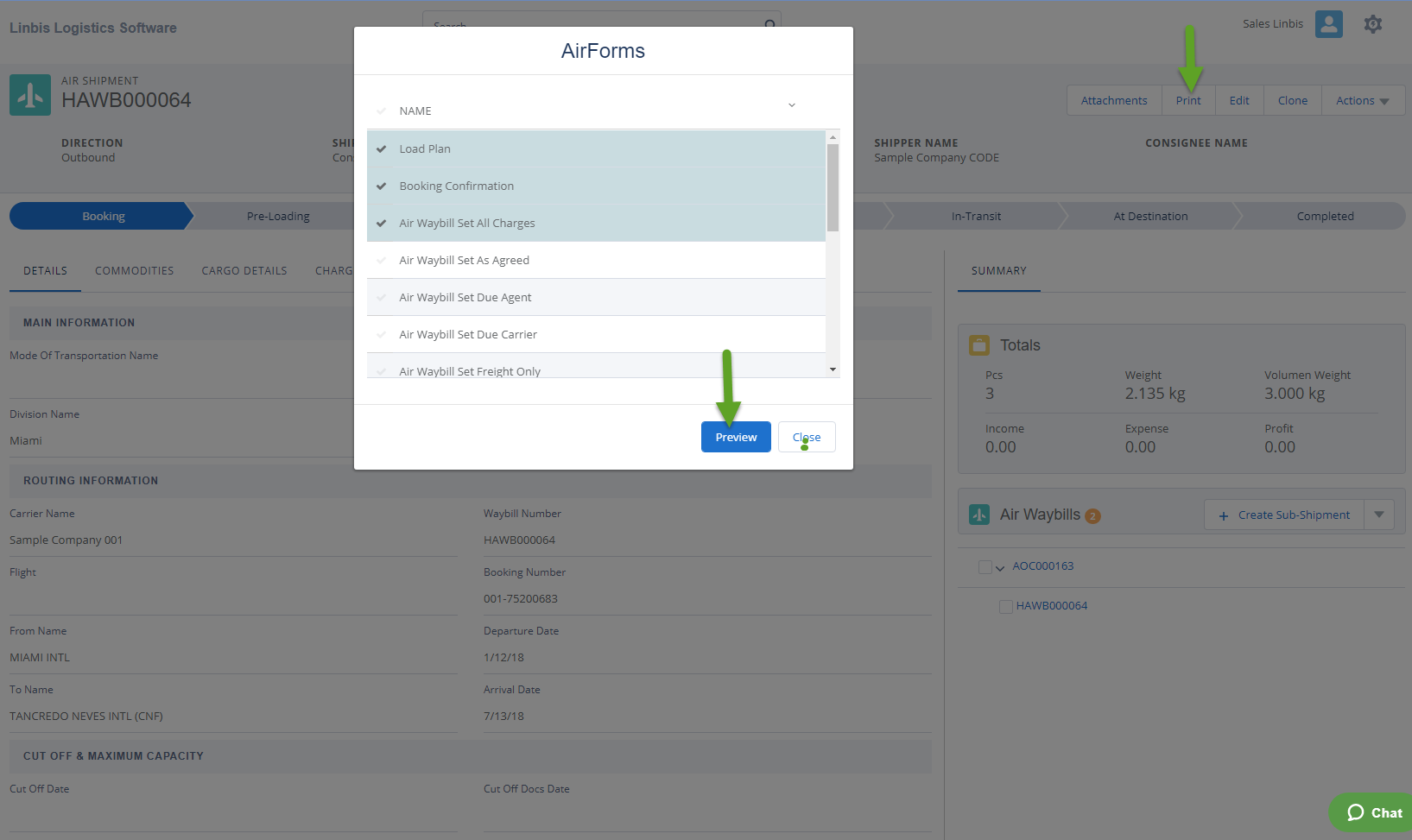





Features of Our Software:
Automated generation of air waybills.
Real-time tracking of shipments.
Compliance checks for international shipping.
Whether you’re a seasoned freight forwarder or a student eager to learn about air freight documentation, our logistics management software offers comprehensive tools and resources to make air freight management seamless.
What is a House Air Waybill (HAWB)?
The HAWB is issued by a freight forwarder to the shipper as a receipt of goods, which consolidates multiple shipments into one master load. This document accompanies the cargo and the MAWB for internal tracking.
HAWB vs MAWB: Understanding the Differences
While both are crucial in the air freight process, they serve different purposes and are used by different parties:
A MAWB is issued by the main carrier of goods, while a HAWB is issued by a freight forwarder.
A MAWB is a contract of carriage with the airline, while a HAWB is used for cargo tracking and control by the freight forwarder.
A MAWB is non-negotiable, whereas a HAWB can be negotiated and endorsed.
Why These Documents Matter
- Legal Compliance: They ensure all parties are compliant with international air transport regulations.
- Cargo Tracking: They provide detailed information about the cargo, helping with tracking and management.
- Customs Clearance: Customs authorities require these documents for processing and clearance.
Features
Streamline Your Air Freight with Our HAWB/MAWB Software
Managing these critical documents can be a daunting task, which is where our freight forwarding software comes in. We provide a robust solution for generating, tracking, and managing HAWB and MAWB efficiently and accurately.
Take the Next Step
Ready to optimize your air freight operations or deepen your understanding of air freight documentation? Explore our logistics software solutions, or access our educational resources today to gain mastery over HAWB and MAWB handling.

The Importance of the Air Waybill (AWB)
The Air Waybill (AWB) is a critical document in the air cargo industry that serves multiple pivotal roles:
Contract of Carriage: It represents the agreement between the shipper and the carrier, stipulating the terms and conditions under which the goods are to be transported.
Evidence of Receipt of Goods: The AWB acts as proof that the carrier has received the cargo as described by the shipper.
Freight Bill: It details the charges related to the transportation of goods and serves as a bill for the freight services provided.
Certificate of Insurance: If insurance is required, the AWB may indicate that the shipment is insured for the duration of the transit.
Customs Declaration: It provides essential information for customs clearance, detailing the nature, quantity, and destination of the goods being shipped.
The Master Air Waybill (MAWB) is a specific type of AWB issued by the main carrier of goods upon receipt from a freight forwarder, with the intent to deliver the goods to the specified destination under agreed terms and conditions. It is a contract of carriage that outlines the obligations and rights of the forwarder and the carrier. The MAWB is a non-negotiable document that serves as the main contract for the movement of goods.
HAWB Issuance by Freight Forwarders
When a freight forwarder or consolidator plays a role in shipping, they issue a House Air Waybill (HAWB) to the shipper as a receipt for the goods. This document, also referred to as the Forwarder’s House Air Waybill, establishes a contract of carriage between the shipper and the freight forwarder. Tools like Linbis Logistics software streamline the creation of both HAWB and MAWB, ensuring accuracy and compliance with shipping regulations.
Upon agreeing to transport the goods, the freight forwarder then secures a contract with one or more airlines. This agreement, documented by the Master Air Waybill (MAWB), details the terms of carriage between the freight forwarder and the airline carriers. The MAWB is critical, especially when multiple modes of transportation are involved, serving as the overarching contract for the entire transit of the goods.
Understanding the Difference Between HAWB and MAWB
The air freight industry uses two principal types of air waybills to document the shipment and carriage of goods: the House Air Waybill (HAWB) and the Master Air Waybill (MAWB).
Master Air Waybill (MAWB): Issued by the main carrier, the MAWB is a contract of carriage between the freight forwarder and the airline. It is an official transport document that outlines the terms agreed upon for the delivery of goods. The MAWB is used for shipments when they are consolidated by freight forwarders and sent to the airline.
House Air Waybill (HAWB): On the other hand, a HAWB is issued by the freight forwarder to the original shipper after receiving the goods and completing any necessary customs formalities. It details the terms for delivering goods to the final destination and is used for the internal tracking of the shipment.
Scenario Illustration: For instance, consider ‘A’ as a freight forwarder who receives cargo from an exporter, ‘X’. ‘A’ agrees to deliver this cargo to ‘B’ in New Jersey. ‘A’ issues a HAWB to ‘X’ upon receipt of the goods. Subsequently, ‘A’ hands over the cargo to ‘C’, the main carrier, who then issues a MAWB to ‘A’, affirming the agreement to transport the cargo to New Jersey.
Here, the HAWB is the document ‘A’ issues to ‘X’, and the MAWB is the document ‘C’ issues to ‘A’.
Legal Standing: It’s important to note that while the HAWB serves as a receipt and contract for shipment, it is not a standalone document of title like the MAWB. The HAWB holds a legal standing similar to the MAWB when it comes to the freight forwarder’s obligations.
Carrier Liability: The MAWB, being signed by the actual carrier (in this case, ‘C’), holds the terms of carriage and assures the consignee of protection in the event of loss or damage to the goods. The HAWB, although outlining the freight forwarder’s terms, does not directly involve the shipper in the carrier’s contract of carriage stated in the MAWB.
What Does AWB Mean in Shipping?
What Does AWB Mean in Shipping?
An AWB, or Airway Bill, is a pivotal document in air freight shipping, serving as a contract of carriage and a receipt of goods between the shipper and the carrier. It’s essential for international shipments and contains details that allow for tracking the shipment’s progress. An AWB is a non-negotiable instrument, meaning it does not convey ownership of the goods, and it specifies that cargo is transported from one airport to another.
Key Functions of an AWB:
- Provides detailed information about the shipment.
- Enables the tracking of the shipment through a unique AWB tracking number.
- Facilitates customs clearance and other transport-related processes.
The AWB is distinguished by its different colored copies, each serving a specific purpose in the documentation process:
- Green: Original – carrier’s copy
- Pink: Consignee’s copy
- Blue: Shipper’s copy
- Brown: Proof of delivery
- White: Additional copies for various administrative purposes
The document only becomes active, meaning the goods are cleared for export, once the required customs formalities are completed.
Differences Between an AWB and a Bill of Lading:
- Issuance: The AWB is issued by an air carrier, while the Bill of Lading is issued by a sea carrier.
- Document of Title: Unlike a Bill of Lading, an AWB is not a document of title. It does not confer ownership and is not negotiable.
- Purpose: Both serve as receipts for goods and contain terms for the carriage, but the Bill of Lading additionally acts as a document of title to the goods.
In essence, the AWB is a key document for air cargo shipments, providing a trail of the shipment for all parties involved, while a Bill of Lading fulfills a similar role for sea freight, with the additional function as a document of title.
