Shipping Container Types Glossary: Choose the Right Box for the Job
This Shipping Container Types Glossary is your quick reference guide to the most common containers in logistics. We’ve included photos, standard dimensions, and best-use cases — plus a handy CTA at the end to try our 🚀 Size-selector tool.
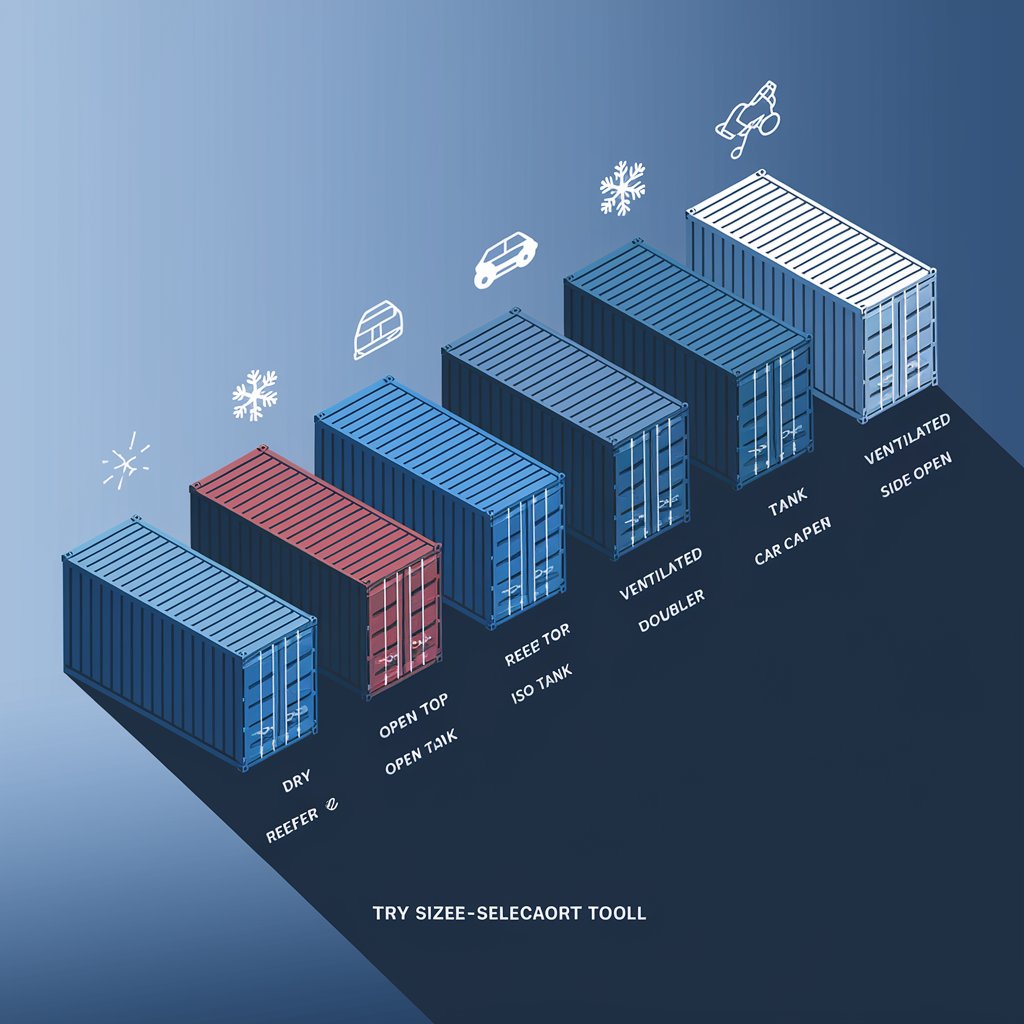
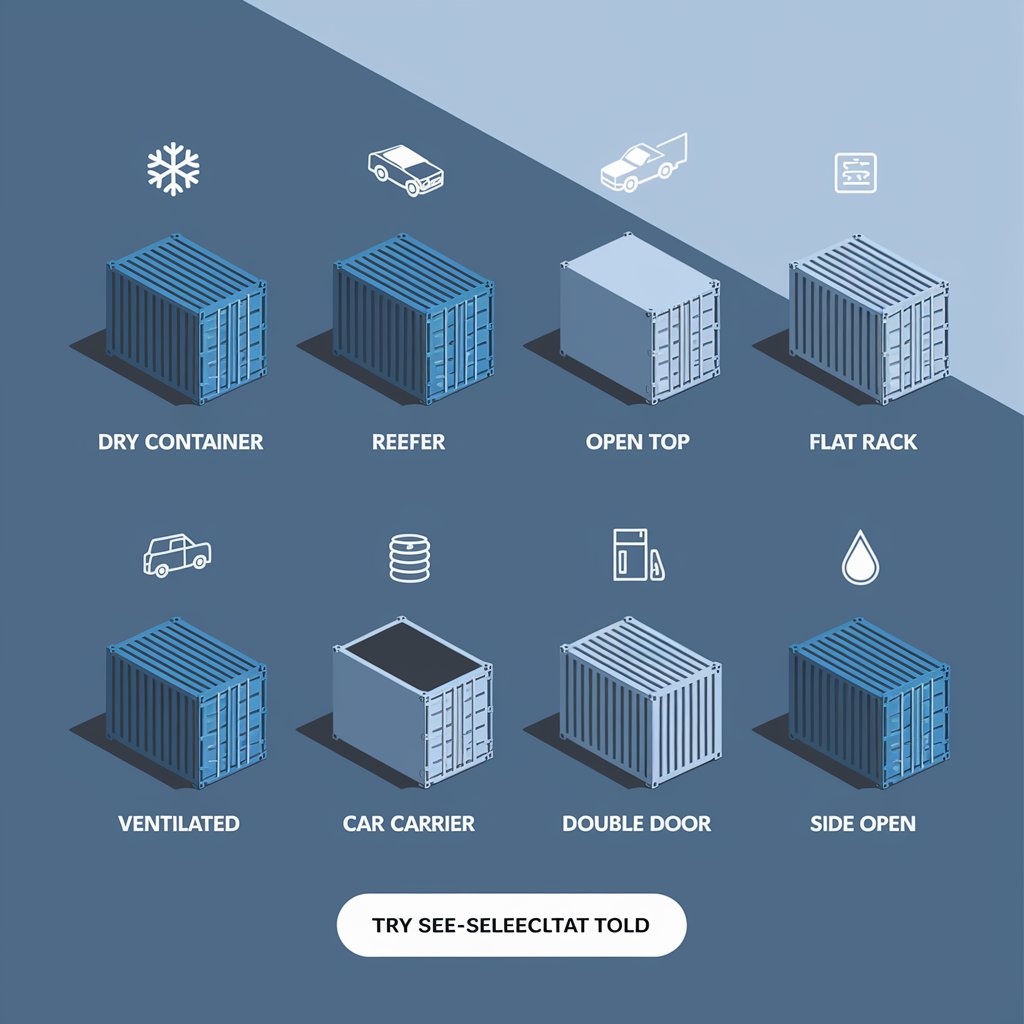
Dry Container (Standard)
Use: General cargo — boxes, pallets, furniture
Sizes: 20 ft / 40 ft / 40 ft High Cube (HC)
Features: Fully enclosed, weatherproof, lockable steel doors
📷 Photo idea: closed steel container in port
✅ Most common. Best for dry, non-temperature-sensitive cargo.
Reefer Container (Refrigerated)
Use: Perishables — food, pharmaceuticals, flowers
Sizes: 20 ft / 40 ft
Features: Built-in refrigeration unit, adjustable temperature
📷 Photo idea: white container with power unit connected
🌡️ Can maintain cargo from -30°C to +30°C.
Open Top Container
Use: Heavy or tall cargo (e.g., engines, generators)
Sizes: 20 ft / 40 ft
Features: Roof covered by removable tarp or bows
📷 Photo idea: container with crane lifting a machine inside
🪜 Allows vertical loading via crane when side access isn’t enough.

Flat Rack Container
Use: Oversized cargo — vehicles, steel coils, machinery
Sizes: 20 ft / 40 ft
Features: No side walls or roof; collapsible ends
📷 Photo idea: open platform with heavy equipment loaded
🔧 Ideal for loads wider or taller than standard container limits.
Ventilated Container
Use: Organic cargo needing airflow — coffee beans, cocoa, logs
Sizes: Typically 20 ft
Features: Passive vents on side panels
📷 Photo idea: container with small ventilation grills visible
🍃 Prevents moisture buildup in goods sensitive to condensation.
Car Carrier Container
Use: Shipping sedans, SUVs, and motorcycles
Sizes: Custom-built or 40 ft container with ramps
Features: Multiple floors or rails, easy loading system
📷 Photo idea: vehicle being loaded into container ramp
🚘 Offers cost-effective vehicle shipping with maximum protection.
Tank Container (ISO Tank)
Use: Liquid bulk — chemicals, wine, oils
Sizes: 20 ft standard frame
Features: Stainless steel tank inside protective frame
📷 Photo idea: cylindrical tank inside a container frame
🧪 Fully sealed. Often used in chemical, food, or energy industries.
Double Door Container
Use: Easy access cargo; staged loading/unloading
Sizes: 20 ft / 40 ft
Features: Doors at both ends for faster handling
📷 Photo idea: container open at both ends
🚪 Improves access in tight warehouse setups.
Side Open Container
Use: Wide or awkward cargo needing side entry
Sizes: 20 ft / 40 ft
Features: Full-length side doors for maximum opening
📷 Photo idea: container with long side open showing pallets
🚚 Useful for forklift loading when front access is limited.
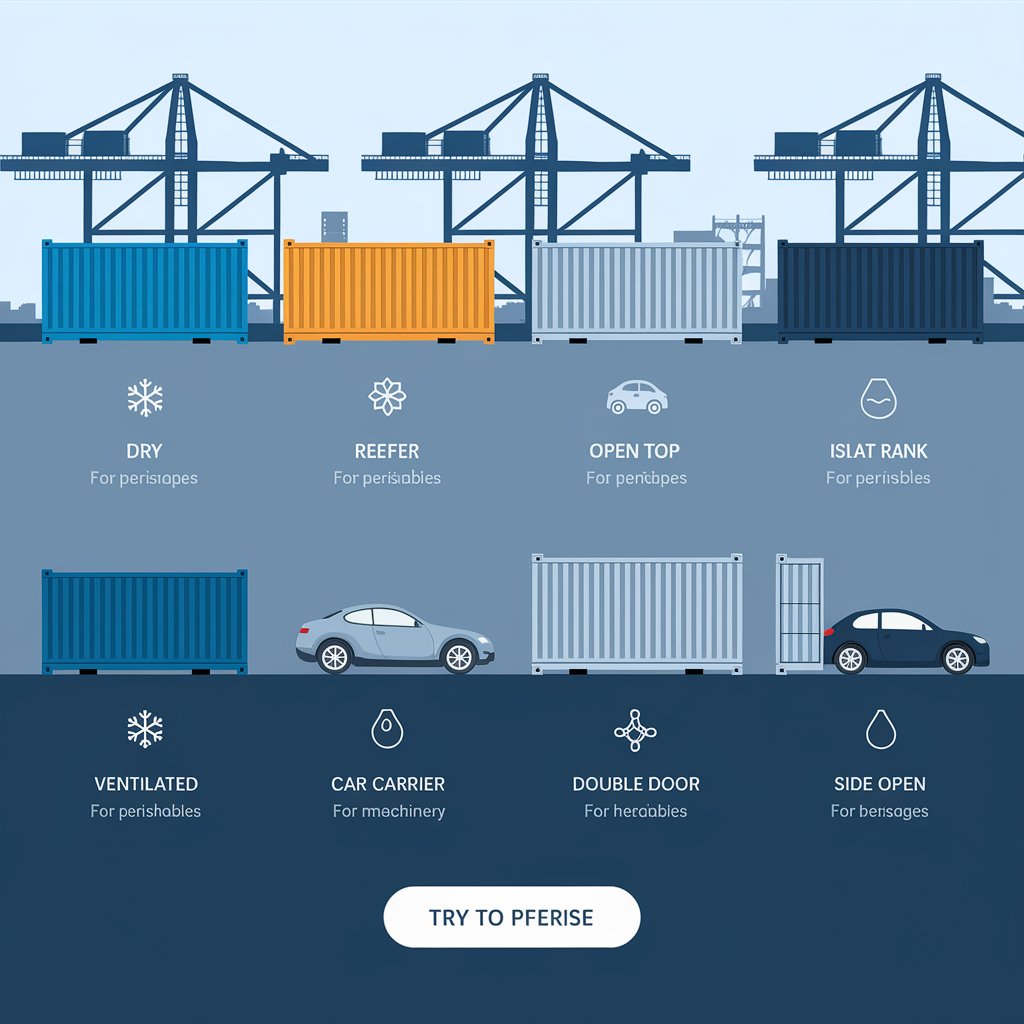
Use Cases by Cargo Type
Cargo Type | Recommended Container Type |
Palletized goods | Dry Container |
Frozen foods | Reefer Container |
Oversized engines | Open Top or Flat Rack |
Vehicles | Car Carrier or Flat Rack |
Chemicals/oils | ISO Tank |
Coffee beans | Ventilated |
✔️ Select the right container = safer, faster, cheaper logistics.
Conclusion: Choose Smart, Ship Smarter
Understanding container types means making smarter shipping decisions — reducing risk, maximizing space, and keeping your cargo compliant with regulations.
Whether you’re handling daily exports or your first shipment, this glossary makes it easy to identify the right container at a glance.
👉 Ready to match your cargo to the perfect container?
🚀 Try our Size-selector tool now and simplify your freight planning.
